Ready-made presentation on the topic of the pre-school program. Pre-school: new priorities of education program of scientific and methodological support of scientific and methodological support of pre-school preparation of children head. Effective component of the model
To use presentation previews, create a Google account and log in to it: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
Pre-school preparation "Rainbow"
OBJECTIVES: to help parents ensure their child’s functional readiness for school; ensure continuity in the training and education of preschool children; create conditions for favorable adaptation of preschool children to school; promote the development of children's cognitive activity, individual intellectual and creative abilities.
main lines of preschool preparation; general development of the child; ability to control oneself voluntarily; formation of positive learning motivation;
identifying the individual characteristics of each child, developing readiness for schooling.
formation of positive learning motivation; development of basic mental functions necessary for successful learning at school (attention, memory, thinking, etc.); development of elementary mathematical concepts; development of speech, phonemic hearing, familiarization with the basics of literacy; development of fine motor skills; formation of manual labor and visual arts skills; development of a creatively active personality.
Intellectual readiness Social and psychological readiness Speech readiness Readiness of children to write
Literacy training. Preparing your hand for writing. Formation of mathematical concepts.
The main objectives of the program: Creating the most favorable conditions for the early identification and development of a child’s abilities. Development of memory, attention, imagination, variability of thinking. Strengthening and developing the child’s emotionally positive attitude towards school and desire to learn.
The main objectives of the course: Enriching the consciousness of children with new content, which contributes to the accumulation of the child’s ideas about the world, prepares him for an elementary understanding of concepts. Introducing children to specific signs, symbols, sign systems; systematization of accumulated and received information through logical operations (analysis, comparison, generalization, classification). Based on the experience of children, to form in them a personal interest and desire to learn.
The main objectives of the program: Development of visual, auditory and semantic memory; Development of imagination and logical thinking; Formation of the ability to carefully and accurately follow the instructions of an adult, to act according to the model; Expanding your general horizons; developing a positive attitude towards school.
Basic skills at the end of the pre-school preparation course: to comply with the rules of behavior at school, to demonstrate your communication skills; count freely within 10 and back; compare numbers within 10, name the “neighbors” of the numbers; solve simple problems; perform graphic dictations; identify sounds in words by ear and characterize them; compose a story based on a picture from 5 to 6 sentences; retell short texts; use pencil, pen, and other graphic materials correctly; listen and follow instructions for the student; apply in practice the simplest ideas about the world around us, use their knowledge to protect their health;
Educational programs Academic subjects Full name teachers Teacher's teaching load per week “Continuity” Teaching literacy Preparing the hand for writing Formation of elementary mathematical concepts 2 2 2 Familiarization with the outside world The world around us 1 Educational games 1 Preschool curriculum “Rainbow”
Tuesday, Thursday 1. 17.00 - 17.25 2. 17.35 - 18.00 3. 18.10 - 18.35 4. 18.45 - 19.10 Call schedule.
Tuesday Thursday 1. Teaching literacy Mathematics 2. Preparing the hand for writing Teaching literacy 3. Mathematics Preparing the hand for writing 4. Educational games The world around us Class schedule
Child Development Center - kindergarten No. 13 “Golden Key”, Salsk Head of the MDOU - Parasotskaya O.V. website
Slide 2
Philosophy of the issue
It is the parents who are responsible for the upbringing and education of children, and all other social institutions are called upon to support, guide, and complement their educational activities (E.P. Arnautova, T.A. Kulikova and others).
Slide 3
Severity of the problem
parents either transfer the preparation of children for school entirely to kindergarten; or they don’t trust preschool teachers and try to solve this problem on their own. Thus, there are discrepancies in understanding the role of interaction between kindergarten and family in achieving a common goal - preparing a child for school.
Slide 4
Target
Organization of management activities focused on creating a space for interaction between teachers and parents in the aspect of pre-school preparation of students
Slide 5
Tasks:
Monitor parents’ ideas about their child’s readiness for school. Develop a model of interaction between teachers and parents in the aspect of pre-school preparation of students.
Slide 6
Methodological basis of interaction
The concept of subject-subject interaction (A.A. Bodalev, N.F. Radionova, etc.). Interaction is considered as a coordinated activity of subjects to achieve joint goals while solving problems that are significant to it. With this approach, the processes of self-development and self-actualization of subjects of education are activated. The concept of the special influence of the family as a social and educational institution on the formation and development of a child’s personality in preschool age. The concept of continuity of the content of education in preschool and primary education (N.F. Vinogradova).
Slide 7
Conceptual idea of experience
Family and preschool are crucial for the socialization of a preschooler, the formation of his personality and preparation for school. Teachers and specialists of preschool educational institutions carry out integrative interaction and cooperation, which is built on the basis of: establishing trusting relationships with parents; discovery of unknown sides and knowledge about their own child to parents; joint involvement of teachers and parents in problems of communication with the child; organizing joint research and shaping the child’s personality at home and in kindergarten; ensuring the child’s overall readiness for school
Slide 8
Monitoring parents’ ideas about their child’s readiness for school
Slide 9
Components of the Parent Engagement Model
Targeted Structural and organizational Contentful Effective
Slide 10
Target component of the interaction model
Creating optimal conditions for interaction with parents, in the aspect of pre-school preparation of students, based on the integration of teachers and specialists
Slide 11
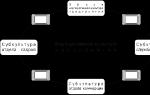
Structural and organizational component of the interaction model
Teacher-psychologist Head of preschool educational institution Physical education instructor Nurse Parents whose children attend a pre-school group Teacher-speech therapist Creative council Pre-school teacher
Slide 12
The structural and organizational component of the model is focused on:
Search and testing of organizational forms of interaction between teachers and specialists of preschool educational institutions with parents, in the aspect of pre-school preparation of pupils
Slide 13
Forms of cooperation
Individual consultations Parent newspaper Parent trainings Thematic consultations “Hotline” Parent evenings Parent rings Test tasks Forum
Slide 14
Parent newspaper section
“Is it time for school?” - includes accessible diagnostic materials that allow parents and teachers to learn how to assess readiness for school and determine the goals of developing school-significant qualities for each child.
Slide 15
Parent newspaper section
“Legal field” - includes legal documents regulating admission to school, the educational process in the first days of school, the interaction of parents with social institutions, etc.
Slide 16
“Difficulties of the first days of school” - includes materials about the course of the adaptation period, problems of adaptation and ways to solve them. The section is interesting and useful for parents and educators.
Slide 17
“Getting ready for school” - includes materials on preparing a child for school in a family environment, educational institutions (kindergarten, development groups at school, additional education institutions). The main attention is paid to materials on the development of arbitrariness, communication skills, decentration, and reflection. Also, a large block of materials is aimed at creating an image of the near future: what school educational programs are available and how to choose them; how to choose a school and teacher; what school supplies will be needed in the first year of study; What should the environment be like for a child going to school?
Slide 18
Test tasks for parents
“Golden Pelican”, based on the results of which the parent determines his competence in preparing his child for school. There are expected to be three (at least) nominations. For example, “Almost Doka”, “Doka”, “Super Doka”. Testing mode is interactive. An official, serious option for testing competence is also possible (through identifying knowledge and skills to solve pedagogical problems and situations)
Slide 19
Slide 20
Stages of the Commonwealth plan-program
Practice-oriented Project-analytical Resultative-reflective
Slide 26
Let's sum it up
An analysis of research and work experience on the problem shows that in modern society it is advisable to build pedagogical interaction between a kindergarten and parents: focusing the goals and content of interaction on current problems of child upbringing and development; using variable forms and methods of parent education; developing parental reflection, focusing on the emotional side of interaction; taking into account the personal experience of parents, appealing to it in the process of interaction; uniting, consolidating parents in the educational process; using the possibilities of the parallel educational process “parents-children”.
Slide 27
May the fruits of your labors multiply!
View all slides
Relevance of the program: The compilation course of developmental activities “Rostock”, for children 6-7 years old, aimed at comprehensively preparing children for school, involves not only the development and availability of certain knowledge and learning skills, but also no less important personal indicators, which are universal educational indicators -important qualities (UUVK) of a future first-grader are the ability to interact in a group of children and with a teacher, understanding and following the rules and norms of behavior at school, the ability to regulate and control one’s emotions in and outside of class, and most importantly, the desire and motivation to learn.

Personal - motivational readiness: includes mastering the skills and abilities to make contact, the ability to interact with other people; differentiation of social status (and, accordingly, relationships): parent, child, adult, teacher; motivational readiness lies, first of all, in the fact that by the time the child comes to school, the dominant desire to play should “grow” into the desire to learn new things, to learn something, the desire to accept educational tasks, to carry out the teacher’s tasks, i.e. study.

Emotional - volitional readiness: at school, the child will face intense academic work; he will be required to do not only what he wants and is interested in, but also what the teacher, the conditions of the school regime, and the training program require. It is especially important for the child to understand the concepts of “good”, “bad”, “possible”, “impossible”; understanding the appropriateness of certain actions in various situations, formed arbitrariness, that is, the ability to act according to a rule, pattern, or teacher’s instructions - these are components of emotional-volitional readiness.

Intellectual readiness: it is important that the child at the beginning of school has a certain level of mental development that corresponds to the age norm of development of a preschooler (harmonious development of the higher mental functions of memory, attention, thinking).




Objectives of the program: To develop preschoolers’ spatial concepts and motor skills. Expand preschoolers’ understanding of the requirements the school places on students, instilling the skills of self-regulation and self-control. To develop students’ skills in constructive communication with future classmates and teachers.



Forms of training: 32 lessons per year (1 time per week); Duration of classes (25 minutes); people in the subgroup aged 6-7 years.



Forms of control: Testing method. - Express diagnostics of readiness for schooling Varkhotova E.K., Dyatko N.V., Sazonova E.V. - Express diagnostics of readiness for school: a practical guide for teachers and school psychologists. – M.: Genesis, 2003).


PRE-SCHOOL: NEW EDUCATION PRIORITIES Program of scientific and methodological support for scientific and methodological support of pre-school preparation of children Program Manager: Korol L.G., Director of the Municipal Educational Institution Methodological Center of Education in Rostov-on-Don Program Coordinator: Ivanova L.G., methodologist MBOU methodological education center of the city of Rostov-on-Don MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION METHODOLOGICAL CENTER OF EDUCATION OF THE CITY OF ROSTOV-ON-DON
PROGRAM CONTENT 1. Section Theoretical substantiation of the issue “Pre-school: new priorities of education.” – Conceptual foundations and the Federal regulatory framework for preschool education. – Domestic and foreign experience – What is pre-school education? – What is “Pre-school preparation”? Goals, objectives, features. – What and how to teach preschool children? – Formation of the necessary knowledge of teachers organizing pre-school preparation of children of senior preschool age. 2. Section Information and analytical information on the organization of preschool education in educational institutions of the city of Rostov-on-Don 3. Section Goal and objectives of the program. 4. Section Program Activities. Expected results. 5. Section Monitoring the professional competence of teachers providing pre-school education Indicators of the level of professional competence of teachers Indicators of the level of pedagogical competence of parents of students. 6. Bibliography section 7. Internet resources section 8. Program Glossary section

1.1. CONCEPTUAL FOUNDATIONS AND FEDERAL NORMATIVE AND LEGAL FRAMEWORK OF PRE-SCHOOL EDUCATION. Conceptual foundations and the Federal regulatory framework of preschool education The Federal Target Program for the Development of Education for the years was approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation for the years, which identified preschool education as a priority direction for its development.

Regulatory framework: - Convention on the Rights of the Child - Constitution of the Russian Federation, Art. Family Code of the Russian Federation - Federal Law from the Federal Law "On Basic Guarantees of the Rights of the Child in the Russian Federation" - Law of the Russian Federation from "On Education" - Federal Target Program for the Development of Education for the Years ( approved by decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated). - The concept of modernization of Russian education for the period until 2010 (approved by order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated r). - Model regulations on a preschool educational institution (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated September 12, 2008 N 666) - Letter from the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation dated /14-15 “On preparing children for school” - Letter from the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation dated /23-16 “ On building continuity in preschool and primary school programs.”

Domestic and foreign experience Since 1994, UNICEF began working together with the governments of various countries to create a system of programs for the development of children of preschool and preschool age at the family and communicative level as an alternative to studying in preschool educational institutions. Turkey - mother education program. A series of films on the development of children from birth to 8 years old, “Parent Education Initiative,” was shown on the Turkish national television channel. Since 1965, the national Head Start program has been operating in the United States, in which approximately 1.3 million volunteers and 1,400 non-profit organizations participate. Since 1959, Cuba has been implementing a national system of educational programs for children of preschool and preschool age in day groups “Teach Your Child”. In the 90s, an experiment took place in Russia to organize groups for short-term stays of children in preschool educational institutions.

“Pre-school education” During the experiment, it turned out that six-year-old children are not ready for learning. At the same time, the problem of coverage with preschool education remained unresolved. That is why in 2004 the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation proposed to discuss ways to equalize the starting opportunities of tomorrow's first-graders. This is how the term “Pre-school education” appeared.

What is preschool education “Preschool education is a term that is widespread throughout the world. But for the Russian ear it is not entirely clear. The concept of education of children of senior preschool age is closer to our traditions.” “Preschool education is the senior stage of preschool, usually lasting two years and designed to soften the child’s transition from kindergarten (as well as any other preschool institution or from the family) to school. But this should not at all turn into the same training of children on first-grade material.”

The success of a child’s life depends on the level of preschool education. Pre-school education ranks third (after higher and primary) in terms of importance. According to experts, due to undeveloped preschool education, the economy loses billions of rubles annually.

Arguments against the immature motivation of six-year-olds to learn the deterioration of children's health the advantage of preschool education programs for preserving the health and emotional well-being of children Data from the Research Institute of Hygiene and Health Protection of Children and Adolescents: compared to the 1980s, the percentage of 6-year-old children who are not ready for systematic education , increased by 5 times% of six-year-olds are mature, more than 49% are moderately mature, and 32.2% are immature in terms of functional readiness for learning.


What is “Pre-school preparation”? Goals, objectives, features. What is “Pre-school preparation”? Goals, objectives, features. The main goal of pre-school preparation is to equalize the starting capabilities of future schoolchildren so that they do not experience stress, complexes, or feelings of humiliation, which can discourage them from studying for all subsequent years (December, 2004). A. Fursenko



Organization of the process of training, education and development of children at the stage of preschool education, taking into account the needs and capabilities of children of this age; selection of the content of education for children at the stage of pre-school education, which will ensure the preservation of the intrinsic value of this period of development, refusal to duplicate the content of education in the first grade of school; TASKS OF PRE-SCHOOL EDUCATION



Thus, the child’s readiness for school presupposes the development of the child’s activity system (choice of means, methods, ability to set a goal and achieve it); broadening his horizons and stimulating cognitive activity; formation of arbitrariness and freedom of behavior; independence, the ability to serve oneself, the ability to communicate with peers and adults. A.A. Leontyev: From five to seven years, as a rule, “leveling out” of health reserves occurs. The main thing is the emergence of new personal formations, such as imagination, mastery of one’s emotions, visual-figurative thinking (formed in a real full-fledged game). D.B. Elkonin: “A child’s readiness for schooling is determined by four lines of his development: 1 line - the formation of voluntary behavior; Line 2 – cognitive activity (mastery of means and standards); Line 3 – transition from egocentrism to decentration; 4th line – motivational readiness.” L.S. Vygotsky: in the second half of preschool childhood, the child is already psychologically ready, if not for school, then, in any case, for the “activity of learning.”

What and how to teach preschool children. TO STUDY the psychological and psychophysiological characteristics of children ready for school; TO DETERMINE the basics of organizing successful training and education of preschoolers and primary schoolchildren TO HIGHLIGHT the personality qualities of a future first-grader MUST NECESSARY:

Psychological and psychophysiological characteristics of children ready for school. School maturity School maturity means the level of morphological, functional and intellectual development of the child, at which the requirements of systematic learning, loads of various kinds, and a new routine of life will not be overly tiring for him.

Physical readiness is a state of health, a certain level of morpho-functional maturity of the child’s body, the required level of development of motor skills and qualities, especially fine motor coordination, physical and mental performance.

Activity, initiative, independence, responsibility, the ability to listen to others and coordinate one’s actions with them, follow established rules, the ability to work in a group. this is a certain level of arbitrariness of behavior, the formation of communication, self-esteem and motivation for learning (cognitive and social); Personal readiness

Development of figurative thinking, imagination and creativity, the foundations of verbal and logical thinking, mastery of the means of cognitive activity (comparison, analysis, classification, generalization, schematization, modeling); native language and basic forms of speech (dialogue, monologue); elements of educational activity within other specifically children's activities (construction, drawing, modeling, various games) Intellectual readiness

The emergence of decentration (taking into account the position of another person when analyzing a situation); the emergence of decentration (taking into account the position of another person when analyzing a situation); identifying a task from the general context of activity, awareness and generalization of solution methods, planning and control; children have ideas about the world of people, things, nature. isolating a task from the general context of activity, awareness and generalization of solution methods, planning and control; children have ideas about the world of people, things, and nature.

Formation of the necessary knowledge among teachers organizing preschool preparation of the psychological and physiological characteristics of children of senior preschool age, consistency in the formation of preschool children’s ideas about themselves, about the world, about objects, about people, i.e. for all sections of the preschool training program, diagnostic techniques for identifying the level of development and formation of ideas of preschool children, their psychophysiological readiness for school;

Formation of the necessary skills among teachers organizing pre-school preparation to diagnose and identify child development problems; carry out corrective work with children to solve identified problems; use various methodological techniques when working with a specific child to ensure the child’s successful progress along the path of his individual development; design individual lessons to achieve specific goals, i.e. select games, materials, create an environment, thinking through the beginning of the lesson, the course and outcome of the lesson, as well as possible situations; Conduct individual lessons that are interesting for a particular child. design group lessons for a specific group of children, select games that are accessible and interesting and be ready to change them as they go; contact with any child without conflicts, be able to quickly establish cooperative relationships, since the time of pre-school preparation is short, and the tasks that need to be solved are very voluminous.

This program is recommended for preschool educational institutions, primary school teachers, parents, and children of senior preschool age. The content of the comprehensive program includes fairy tales of various subjects. The use of fairy tales as the main educational and developmental material in the process of preschool preparation is due to the peculiarities of the age psychology of future first-graders. It is fairy tales that contribute to the formation of educational motives in future first-graders, since they are well known and understandable to children. The content of each fairy tale allows you to solve problems: the development of higher mental functions and arbitrariness of cognitive processes, learning to read and write, the development of phonemic hearing, the development of speech, the development of elementary mathematical concepts, the development of fine motor skills of the hands, the development of imagination and creative abilities. The content of the comprehensive program and the structure of integrated training sessions provide for multi-level training of preschoolers.


Form the personality of a preschool child Develop higher mental functions and cognitive processes Teach literacy Develop phonemic hearing Develop speech Develop elementary mathematical concepts Develop fine motor skills Develop creative abilities