Product profitability characterizes. Profitability of products sold: calculation formula. What can determine the profitability of an enterprise’s products?
Every aspiring entrepreneur is incredibly happy when he receives the first shoots of his work, and this is quite fair. - a difficult path that requires great expenses in every sense of the word. Why do some of them suffer subsequent disappointment? After all, the idea is great, the products are in demand, the equipment is set up, and the staff has already learned how to work? The problem is that production costs constantly exceeded sales profits, and the initial capital melted like an iceberg in Africa.
The main result of the activity of any enterprise was and remains. Achieving this indicator depends on many factors:
- Income from sales of manufactured products (or services of the enterprise).
- Production costs: utility bills, payments and interest on loans, tax obligations, materials and equipment, payments to employees and subcontractors, etc.
The profitability of an enterprise allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of its activities and consists of the total result of profitability:
- Sales (product sales), if the organization produces goods in an assortment, then it is necessary to calculate the profitability for each type of product.
- , here we mean all the company’s property (transport, real estate, equipment, etc.) without taking into account borrowed funds and debt obligations.
- Own capital.
- Investments and loans.
In addition to the production and sale of products, a company may be engaged in any other work: providing services, investing, or being a borrower. Any of these operations will generate revenue or increase costs, which in turn affect the profitability of the organization. Therefore, it is very important to evaluate each of these components separately, which will allow you to identify weaknesses and correct the situation in a timely manner.
Sales profitability depends on many factors:
- commodity unit, production costs
- Buyer activity and demand for products
- Competitiveness, quality and attractiveness of the product for the consumer
- Pricing policy and market value of a commodity unit
This value is calculated as a percentage and shows how much profit the organization received over a certain period of time from each ruble spent on the production and sale of a particular product. Also, this financial indicator is an assessment of the effective management of the enterprise, because making a profit directly depends on the right decisions of management.
Calculation formula and main indicators
So, in the process of its activities, an enterprise expends resources, and as a result makes a profit. The ratio of profits to costs is the profitability ratio of the enterprise. As for the profitability of products sold (sales), it is determined by the following formula:

Where RRP is the return on sales ratio, PP is the profit from sales, SBS is the cost of goods sold.
The correctness and accuracy of the calculations lies in what types of profit and costs are included in them. It is also necessary to clearly define the period for which the calculation will be made. If profits are calculated for one month and costs for another, then the result obtained will be incorrect and useless.
It will not be entirely correct to use the net profit of an enterprise in calculations if the company receives income from several types of activities, and not each of them is related to the sale of products. In this case, you need to take as a basis only profit from sales, which is easy to find in. If you need to determine the profitability ratio of sales of a certain product group or type, you will have to calculate sales revenue for the selected period of time specifically for a specific product category.
Now you need to decide on the cost. This indicator has two main forms: production and complete.
Production costs consist only of the costs of manufacturing products (raw materials, materials and other resources), but do not include sales costs. Operating with this figure is also not entirely correct, since the result obtained will be overestimated and not relevant enough. The calculations should be based on the full cost, which consists of the costs of both production and sales.
The accuracy and reliability of the result will depend on the choice of the correct main indicators, without which the analysis and further calculations lose their meaning.
Calculation examples and conclusions

For a more complete perception of this information, you should consider a visual one: the company produces chocolate and candies. Sales revenue for the selected period amounted to 560,000 rubles, the total cost, including all expenses, was 243,000 rubles. It is necessary to calculate the profitability of products sold.
First, you should determine the profit from sales; to do this, you should subtract costs from revenue: 560,000-243,000 = 317,000 rubles. Next, we calculate the return on sales ratio: 317000/243000 = 1.3045, round the result to hundredths, it turns out 1.30.
To determine the amount of profit from each ruble for products sold, this is multiplied by 100, 1.3*100=130 (kopecks). It turns out that every ruble spent brings 1 ruble 30 kopecks to the company’s profit. This can be considered a very good result.
Now an example of a more detailed calculation. The company produces chocolate bars, boxed and weighed chocolates.
Profitability for each product group for each ruble spent, respectively: 0.86 rubles, -0.34 rubles, 0.78 rubles. It turns out that the production of boxed sweets is unprofitable for the enterprise and should either be stopped or revised: increase the market value, reduce costs, etc. Sometimes the company's management decides to carry out promotions, that is, costs increase for a certain time, but subsequently there is a positive trend.
The profitability threshold is considered to be zero, when costs are covered, but the enterprise does not make a profit. This trend is typical for new firms whose products are not yet in high demand, investments have not yet paid off and there is a constant need for advertising costs. If this indicator remains zero or negative for a long time, the situation should be analyzed and weaknesses identified.
Sales profitability analysis
There is no regulatory framework for the profitability ratio of products sold. This financial indicator is determined by comparison:

- With sales of competing companies
- With previous indicators and dynamics in general
- Compliance with previously drawn up forecasts and plans
Competitiveness has always been the key to a successful business. It is almost impossible to achieve good results in the modern market without looking at competitors. For this purpose, regular monitoring of certain product groups is carried out. Basic methods of maintaining competitiveness:
- Flexible pricing policy. An exorbitantly inflated price leads to a decrease in consumer demand, and an understated price will not bring profit. It is very important to find a middle ground here in order to stay afloat among competitors.
- Constant control of product quality. Without paying attention to this issue, you can lose all your clients and customers.
- The attractiveness of the product for the buyer. All means are good here: colorful practical packaging, high-quality advertising, etc. Many companies provide retail outlets with equipment for their products in order to present them in the most favorable light to the consumer.
A rather unstable financial indicator that needs to be constantly monitored. The easiest way to analyze the situation is using graphs or a table where data is entered for each reporting period; this will allow you to quickly and clearly track the dynamics of profitability.
If this financial indicator is prone to decline and does not correspond to pre-developed plans, it is necessary to identify the reasons for this trend and take measures to eliminate them. The methods can be very diverse, but they have two main directions: reduce costs and increase profits.
Profitability of products sold is the main indicator that evaluates the company's activities. This aspect is important both for the owner of the enterprise and for investors, creditors and business partners, so it must be monitored constantly and very carefully.
Write your question in the form below
The product profitability formula will show whether the enterprise is making a profit or operating at a loss. It will show how much profit one ruble invested in production brings.
[Hide]
What is product profitability?
When organizing a service company, calculating the product profitability formula will show how effectively funds are spent and how much income the company brings.
When obtaining information on profitability, the assets of the enterprise are not taken into account. The calculation involves only data on current profits and costs.
User Olya Skazala talks about the types of profitability and how to calculate it.
What determines the profitability of an enterprise's products?
Product profitability depends on factors:
- Changes in product structure. If the overall structure is dominated by the sale of more profitable products, the average indicator increases.
- Commodity prices. When the price of a product changes, its profitability also changes.
- Changes in the cost of goods. When the cost of goods changes, the profitability indicator also changes.
Why do you need to calculate product profitability?
Based on the profitability indicator, he can determine:
- which product is in greatest demand;
- How profitable is the production of a particular product?
How to calculate product profitability and when to do it?
- Drawing up a business plan. To calculate profitability, it is necessary to monitor the market and calculate planned costs and profits.
- In fact, work. The profitability of a business can exceed the entrepreneur’s expectations, or it can lead to bankruptcy if costs are not adjusted in a timely manner.
There are basic formulas for calculating profitability:
- general;
- balance sheet.
General formula
The general calculation formula takes into account the following indicators:
- profit from product sales;
- cost of production.
General formula for calculating profitability
The formula can take into account profit:
- from sales;
- clean.
The cost can be:
- full;
- production.
Using this formula, the profitability ratio can be calculated for the periods:
- month;
- quarter;
- some years.
Using different periods, they look at the dynamics of the indicator and calculate the average.
The general formula is not tied to the specifics of accounting. It is suitable for calculating profitability when drawing up a business plan.
Formula for calculating product profitability on balance sheet
When calculating the profitability of products on the balance sheet, the data available in Form No. 2 (financial results report) is taken into account.
Product profitability formula:
Based on net profit at full cost By profit from sales and total cost By net profit and production cost By sales profit and production cost
When calculating profit from sales, a return of 12% is considered normal. Depending on the industry of production, the calculation result may vary. Therefore, practitioners recommend comparing the results obtained with the industry average.
Examples of calculations
As an example, profitability can be calculated for an enterprise with the following economic parameters:
- the enterprise produces one type of product;
- total sales revenue - 5,000,000;
- production costs - 3,300,000.
To check profitability, you need to find the total profit: 5,000,000 - 3,300,000 = 1,700,000.
To calculate the profitability ratio, the general formula is used: 1,700,000/3,300,000*100% = 0.51(51%).
This calculation shows that every ruble invested in production brings 51 kopecks. If you compare the results obtained with previous periods, you can see the dynamics of the competitiveness of the product.
Also, as an example, we can consider the same enterprise, subject to the production of several types of products:
- total revenue from sales of 1 product - 1,000,000;
- production costs of 1 product - 700,000;
- total revenue from sales of 2 products - 1,500,000;
- production costs of 2 goods - 900,000;
- total revenue from sales of 3 products - 900,000;
- production costs of 3 goods - 1,100,000.
Calculation of profitability of 1 product:
- profit from sales: 1,000,000 – 700,000 = 300,000;
- profitability: 300,000/1,000,000*100% = 0.3 (30%).
Calculation of profitability of 2 goods:
- profit from sales: 1,500,000 – 900,000 = 600,000;
- profitability: 600,000/1,500,000*100% = 0.4 (40%).
Calculation of profitability of 3 products:
- profit from sales: 900,000 – 1,100,000 = - 200,000;
- loss: 200,000/900,000*100% = 0.22 (22%).
Analyzing the profitability indicators, it is clear that the company will receive greater profits when increasing the production speed of the second product.
As for the losses of the third product, the situation can be improved:
- reducing the cost;
- carrying out marketing activities and increasing sales.
If these measures do not help, it is better to discontinue the product.
How to analyze indicators?
Cost-benefit analysis is necessary for:
- Determination of production cost efficiency. It is calculated based on the technological cost. The resulting figure will be higher than when calculating at full cost.
- Determining the cost efficiency of production and sales. This parameter is calculated based on the full cost indicator.
Analysis and comparison of these figures will allow you to see how much costs are incurred at each stage.
Unlike profit, which shows the absolute effect of activity, there is a relative indicator of the efficiency of an enterprise - profitability. In general, it is calculated as the ratio of profits to costs and is expressed as a percentage.
The following types of profitability are distinguished:
1) profitability of production (production assets)(R p), calculated by the formula:
R p = P in / (GPP + NOS),
where P in is the total (gross) profit for the year (or other period);
GPP - average annual cost of fixed production assets;
NOS is the average annual balance of standardized working capital.
2) return on equity(R s.k), which is characterized by the size of the authorized capital (share capital), it interests all shareholders, because determines the upper limit of dividends:
R s.k = P h / K s,
where P h - net profit (including interest payments on the loan);
Kc is equity capital, the value of which is taken according to the balance sheet and is equal to the amount of assets minus debt obligations.
3) return on permanent capital(R p.k) - reflects the efficiency of using long-term (permanent) capital in the organization’s activities (both own and borrowed):
R p.k = P h / K p,
where K p is permanent capital.
4) return on total assets(P a) - characterizes the efficiency of using all available assets of the enterprise:
R a = P h / K a,
where K a is the average amount of assets on the enterprise’s balance sheet;
5) product profitability(P pr) characterizes the cost efficiency of its production and sales:
R pr = P r / S r,
where Pr is profit from sales of products (works, services);
Ср - full cost of goods sold;
6) profitability of certain types of products(R v.pr):
R v.pr = P unit / S unit,
where P ed - profit per unit of production;
C unit - the total cost of a unit of a certain type of product;
7) profitability of sales (sales or turnover)Р р - shows the share of profit per one monetary unit of sales (cost of products sold):
P r = P r /V r,
where P r – profit from sales;
V r – sales revenue.
They are obtained by dividing the profit from the sale of products by the amount of revenue received. The initial data for its calculation is the balance sheet.
It is calculated in the FinEkAnalysis program in the Profitability Analysis block as Return on Sales.
Profitability of products sold - what it shows
Shows how much profit the company receives from each ruble of products sold.
Profitability of products sold - formula
General formula for calculating the coefficient:
Calculation formula based on the old balance sheet data:
| K ppp = | page 050 | *100% |
| p.010 |
Where page 050 And page 010 profit and loss statement (form No. 2).
Calculation formula based on the new balance sheet:
Return on products sold - value
It is used as the main indicator for assessing the financial performance of companies with relatively small amounts of fixed assets and equity capital. Assessing the profitability of sales makes it possible to objectively look at the state of affairs.
The return on sales indicator characterizes the main aspect of the company's work - the sale of main products.
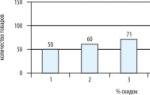
Profitability of products sold - diagram
1. Increasing the indicator.
a) Revenue growth rates outpace cost growth rates. Possible reasons:
- increase in sales volumes,
- change in sales mix.
With an increase in the number of products sold in physical terms, revenue increases faster than costs as a result of production leverage.
The components of product cost are variable and fixed costs. Changing the cost structure can greatly affect profit margins. Investing in fixed assets is accompanied by an increase in fixed costs and, theoretically, a decrease in variable costs. Moreover, the relationship is nonlinear, so finding the optimal combination of fixed and variable costs is not easy.
In addition to simply raising prices for its products, a company can increase revenue by changing its product mix. This trend in the development of the enterprise is favorable.
b) The rate of cost reduction is faster than the rate of revenue decline. Possible reasons:
- increase in prices for products (works, services),
- change in the assortment structure.
In this case, there is a formal improvement in the profitability indicator, but the volume of revenue decreases; the trend cannot be called unambiguously favorable. To correctly draw conclusions, analyze the pricing policy and assortment policy of the enterprise.
c) Revenue increases, costs decrease. Possible reasons:
- price increase,
- change in sales mix,
- change in cost standards.
This trend is favorable, and further analysis is carried out to assess the sustainability of this position of the company.
2. Decrease in indicator.
a) The growth rate of costs outpaces the growth rate of revenue. Possible reasons:
- inflationary growth in costs outpaces revenues,
- price reduction,
- change in the structure of the sales range,
- increase in cost standards.
This is an unfavorable trend. To correct the situation, they analyze the issues of pricing at the enterprise, assortment policy, and cost control system.
b) The rate of revenue decline is faster than the rate of cost reduction. Possible reasons:
- reduction in sales volumes.
This situation is common when an enterprise reduces its activities in the market. Revenue declines faster than costs as a result of operating leverage. An analysis of the company's marketing policy should be made.
c) Revenue decreases, costs increase. Possible reasons:
- price reduction,
- increase in cost standards,
- changing the structure of the sales range.
An analysis of pricing, cost control systems, and assortment policy is required.
In normal (stable) market conditions, revenue dynamics change faster than costs only under the influence of production leverage. The remaining cases are associated either with changes in the external and internal conditions of the enterprise’s functioning (inflation, competition, demand, cost structure), or with an ineffective system of accounting and control in production.
Was the page helpful?
Synonyms
More found about profitability of products sold
- Patterns and trends in the financial results of small and medium-sized enterprises
The article discusses the results of the analysis of such indicators of the activity of micro-enterprises of small and medium-sized enterprises as the balanced financial results of the enterprises, the share of profitable and unprofitable enterprises, the profitability of manufactured and sold products, the existing levels of profit and loss per unit, respectively - On the standard values of coefficients when forming a rating assessment of the financial and economic condition of an enterprise
Vp and profitability of sold products Rp for the period 2005-2012 according to the Russian statistical daily are presented in - Analysis of consolidated and segment reporting: methodological aspect
In the process of analysis, an assessment is made of financial stability, debt capital concentration ratio, solvency, maturity of obligations, efficiency of current activities, return on products sold and return on sales, intensity, asset turnover ratio and efficiency, return on assets and profitability. - The influence of individual elements of accounting policies on reporting items and financial performance indicators
Profitability indicators - profitability of products sold Ррп Shows the effectiveness of the costs incurred by the enterprise for the production and sale of products - - Profitability: To be managed, it must be measured correctly.
The profitability of all commercial products is determined as the ratio of profit per commodity output to the cost of commercial products. The profitability of all products sold is calculated as the ratio of profit from sales g to the total cost of products sold. - Methodology for managing the financial results of an enterprise
Indicators of product profitability reflect the efficiency of current costs, in contrast to the overall profitability indicator characterizing the efficiency of advanced capital, and are calculated as the ratio of profit from product sales to the total cost of products sold. The profitability of a particular type of product depends on the prices of raw materials, the quality of the product, and labor productivity. - Multi-criteria approach to business risk analysis
LLC Kuban The profitability of sales in 2013 compared to 2011 increased by 0.863 points and compared to 2012 - decreased by 3.308 points The profitability of products sold has a similar development trend in the period under study In 2013, this indicator - Factor analysis of the formation and use of company profits
The decrease in the ratio can be explained by a significant increase in the amount of equity capital in 2016; the growth rate of profit is lower than the growth rate of the enterprise’s equity capital, due to which the return on capital indicator in 2016 decreased the last year’s figure by 5 kopecks. The main reserves for profit growth... The main reserves for profit growth of the organization are a decrease cost of goods sold increasing the volume of its sales improving the quality of products selling them on more profitable markets - Working capital management policy in the holding
Profit margin on sales PMOS is the ratio of net profit to revenue - Gross profit management of a modern manufacturing enterprise as an integral condition for corporate profit management
Vph -Vpo Iv In the second case, the difference between the basic level of profitability calculated based on the actual volume and range of products sold and its basic level is multiplied - Analysis of the capital structure and profitability of leading Russian oil and gas enterprises
Return on sales allows you to find out how much profit falls on a unit of sold products. Return on equity capital characterizes the efficiency of using equity capital and influences the level of - Features of factor analysis of performance indicators of an economic entity
By successively replacing the planned base level of each factor indicator with the actual one and comparing the calculation result before and after replacing each factor, it is possible to determine the change in the level of profitability due to the volume of products sold qtotal structure UDi prices p specific variable costs - The associated effect of operational and financial leverage in managing the financial condition of an organization
This indicator is needed to find out how much products need to be sold in order to fully cover its costs. For JSC Tander, the profitability threshold in the reporting year - Profitability of gross output
Profitability of gross output shows how much gross profit is in each ruble of sold products, works, services Profitability of gross output - formula General formula for calculating the coefficient Krvp Gross - Assessing the efficiency of using financial resources of organizations in the regional agricultural sector
This indicates an increase in the efficiency of using equity capital. Return on sales is calculated by dividing gross profit by the volume of products sold. In 2011, this - Gross Margin
Gross profitability shows how much gross profit is in each ruble of sold products, works, services Gross profitability - formula General formula for calculating the coefficient KVR Gross profit - Analysis of financial results (based on materials from Ganymed SB LLC)
Calculation of the return on sales indicator showed that in 2013, per unit of products sold by Ganimed SB LLC there were - Profit and profitability indicators
In this regard, the most important indicator reflecting the performance of an enterprise is profitability, which characterizes the profitability of the activity relative to the funds advanced or the volume of turnover for products sold. To quickly calculate profitability and profit indicators, use the financial analysis program FinEkAnalysis Example. - Multilevel factor analysis of agricultural producer business activity indicators
B - sales revenue Return on sales shows how much profit falls on a unit of sold products Its economic meaning lies in - Such different goodwill: testing various methods for assessing a company’s goodwill and interpreting the results obtained
Qf - cost of sales of goods, works, services Rq - industry average coefficient of profitability of product sales Rg - coefficient
The desired result of every enterprise is profit. However, profit in absolute terms (in rubles, thousands or millions) is just a number on the income statement. For the owner or investor, it is, of course, important, but not informative enough. In order to understand how hard this profit was obtained, there are relative indicators of profitability, called profitability indicators. One of them is production profitability.
Profitability of production correlates the amount of profit received with the amount of funds that made it possible to obtain it, shows the amount of profit per 1 ruble. spent production assets. The fewer funds are used to obtain a certain amount of profit, the higher the profitability of production, and therefore the higher the efficiency of the company.
Read our articles about other profitability indicators:
- “Determining return on assets (balance sheet formula)”
- “Determining return on equity (formula)”
Production profitability formula
Profitability of production is the ratio of the total amount of profit (balance sheet profit) to the average annual cost of fixed and working capital.
The formula for calculating production profitability is as follows:
Rproduct = Pr / (OF + ObS) × 100,
Rproduct—production profitability;
PF - average cost of fixed production assets for the billing period;
OBC is the average cost of working capital.
Where to get the numbers for calculations
Information for calculating production profitability is taken partly from financial statements and partly from accounting analytics.
Thus, we obtain the amount of balance sheet profit from the statement of financial results - from line 2300 “Profit (loss) before tax” of Form 2.
Read more about this report in the article “Filling out Form 2 of the balance sheet (sample)” .
Data for the denominator of the fraction will most likely have to be looked for in analytical accounting registers. It is unlikely to be possible to take figures from the balance sheet. For example, because it reflects aggregate data on the enterprise’s fixed assets, and to calculate the profitability of production, the balances of production assets are needed. This means that detailed information about the OS is needed.
Production profitability, product profitability and sales profitability - is there a difference?
Of course there is. These are separate types of profitability, three independent indicators. It has already been said above that production profitability shows the share of profit per 1 ruble. spent production assets.
In turn, product profitability shows the amount of profit per 1 ruble. cost (full or production). It is calculated using the formula:
Rpr = Pr / Ss × 100,
where: Rpr - product profitability;
Pr - profit;
CC - cost price.
As for the profitability of sales (it is also called total profitability), it carries information about the amount of profit per 1 ruble. revenue. It is calculated using the formula:
ROS = Pr / Op × 100%,
where: ROS - return on sales;
Pr - profit;
Op - sales volume or revenue.
As you can see, the indicators really differ both in meaning and in calculation. And they should not be confused.